Abstract: This paper mainly introduces the use of Delta VE inverter in CNC machining center.
Key words: CNC machining center positioning VE inverter Delta pulse given
1 Introduction
CNC machine tools are the key equipment of modern manufacturing. The output and technical level of a national CNC machine tool represent the manufacturing level and competitiveness of this country to some extent. There is still a big gap between the technical level, performance and quality of CNC machine tools in China compared with foreign products. Most high-performance machining centers and features rely on imports. The machining center is a concentrated expression of numerical control technology. The market is active and demand is strong, which has become the frontier of the current and future CNC machine tool market.
The machining center is a digitally controlled machine tool that has a tool magazine and can automatically change tools and process multiple workpieces. After the workpiece is clamped once, the digital control system can control the machine tool to automatically select and replace the tool according to different processes, automatically change the spindle speed of the machine tool, the feed amount and the movement track of the tool relative to the workpiece and other auxiliary functions, and successively complete several faces of the workpiece. Processing in multiple processes. Due to the concentration of the process and automatic tool change, the machining center reduces the time for workpiece clamping, measurement and machine adjustment, so that the cutting time of the machine tool reaches about 80% of the machine start time (only 15-20% for ordinary machine tools); It also reduces the workpiece turnover, handling and storage time between processes, shortens the production cycle, and has obvious economic benefits. The machining center is suitable for small and medium-sized batch production with complex parts, high precision requirements and frequent product replacement. The first machining center was first developed in 1958 by the American Carney-Trek company. It adds an automatic tool changer to the CNC horizontal boring and milling machine, which enables centralized machining of various processes such as milling, drilling, boring, reaming and tapping after the workpiece is clamped once. Since the 1970s, the machining center has developed rapidly, and a changeable spindle box machining center has appeared. It is equipped with a multi-axis spindle box with tools that can be automatically replaced, which can simultaneously process the workpiece. This multi-process centralized machining form has also been extended to other types of CNC machine tools, such as turning centers. It is equipped with multiple automatic tool changers on a CNC lathe that can control more than three coordinates. In addition to turning, the spindle can be stopped. Or indexing, milling, drilling, reaming and tapping by tool rotation, suitable for machining complex rotating parts. Machining centers are divided into vertical and horizontal types according to the arrangement of the main shaft. The horizontal machining center generally has an indexing turntable or a numerical control turntable, which can machine each side of the workpiece; it can also be used as a joint motion of multiple coordinates to process complex spatial surfaces. Vertical machining centers generally do not have a turntable and are only used for top surface processing. In addition, there are composite machining centers with vertical and horizontal spindles, and vertical and horizontal adjustable machining centers with spindles that can be adjusted to horizontal or vertical. They can machine five faces on the workpiece. The automatic tool changer of the machining center consists of a tool magazine and a tool changer that store the tool. There are many types of tool magazines, and there are two types of discs and chains. The chain knife stocking tool has a large capacity. The tool change mechanism exchanges the tool between the machine tool spindle and the tool magazine. The common one is the robot. There is also a tool that does not have a robot and the spindle directly exchanges the tool with the tool magazine. In order to further shorten the non-cutting time, some machining centers are equipped with two pallets for automatically exchanging workpieces. One is loaded with the workpiece on the workbench, and the other is loaded and unloaded outside the workbench. After the machine tool completes the machining cycle, the pallet is automatically exchanged, so that the loading and unloading of the workpiece coincides with the machining time.
2 CNC machine spindle drive
The spindle drive system is a high-power actuator for CNC machine tools. Its function is to accept the S code speed command of the CNC system and the M code auxiliary function command to drive the spindle for cutting. The drive of the main shaft can be controlled by AC frequency conversion or AC servo. The general AC variable frequency spindle can be steplessly changed but cannot be stopped. It needs to be equipped with a spindle position sensor to match the logic of the CNC system PMC (index control system built-in PLC). The program completes the quasi-stop speed control and positioning stop; the AC servo spindle itself has the quasi-stop function, its own axis control PLC signal can be directly connected to the PMC of the CNC system, and the quasi-stop positioning control can be completed with the simple PMC logic program. The latter's control accuracy is much higher than the former, so the spindle drive system of most machining centers currently adopts the AC servo spindle. With reference to the functions of the AC servo spindle, Delta has developed a new generation of AC variable frequency drive - VE inverter, which is comparable to AC servo in terms of function and performance, but also has versatility and price advantage. The test won the recognition and love of customers.
3 Delta VE variable frequency spindle drive system 3.1 System design requirements
(1) Numerical control characteristics of function and performance of VE series inverters. The project customer is a well-known enterprise of CNC machining center. In combination with the requirements of customers and the characteristics of the machining center, Delta's high-performance inverters developed for CNC machining centers---VE series inverters are very suitable for use in CNC machining centers:
· Fast single point positioning through external I/O points, characteristic curve adjustment and positioning time with special parameters adjustment, which is convenient for implementation;
· Achieve rapid acceleration and deceleration through special parameter adjustment;
· New PDFF control makes the adjustment of gain easier and easier to master;
· Accept analog signals and pulse signals, and support the host computer more comprehensively.
(2) Test machining center configuration:
·CNC system: Taiwan's new generation CNC system SYNTEC 9401;
·Spindle specification: Wuxi Bohua motor 8kw / maximum frequency 600hz-12000rpm/6P/380V/450hz/25A, encoder +5V/GND/+A/-A/+B/-B/+Z/-Z/512ppr ;
· Inverter specifications: 075V43A-2+EMV-PG01L, software version 9.98 test version, braking resistor 1500W/75ohm.
3.2 Spindle frequency conversion system design
(1) Inverter electrical design: See Figure 1.
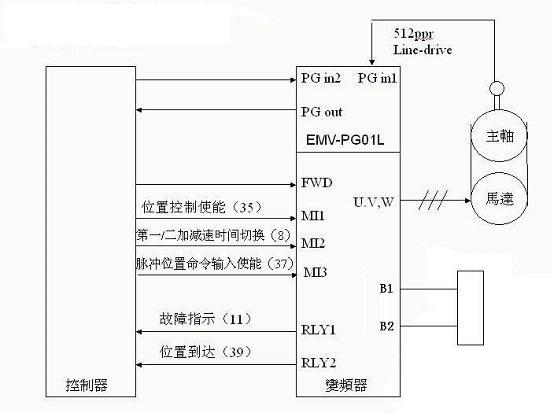
Figure 1 Inverter wiring diagram
Next page



